What are the Strategies to Scale a Business?
by David McKenna
What are the Strategies to Scale a Business?
Scaling a business can be achieved through four key strategies: utilising existing products, developing new products, targeting current markets, or expanding into new markets. These aspects are outlined in a planning tool known as the Ansoff Matrix, which provides a framework for analysing and planning growth strategies. By leveraging the strategies outlined in the Ansoff Matrix, businesses can achieve significant growth metrics such as increased sales revenue, improved customer loyalty and retention, reduced customer acquisition costs, and higher lead-to-client conversion rates. Let’s explore each strategy in more detail.




Ansoff Matrix and the Four Growth options
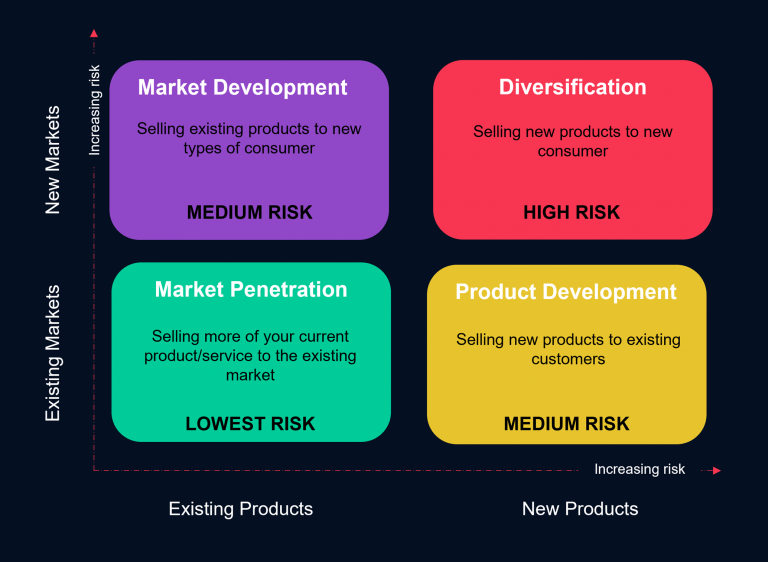
Each quadrant of the Ansoff Matrix corresponds to a specific growth strategy. These strategies are:
- Market Penetration– Increasing sales of existing products into an existing market
- Market Development– Increasing sales existing products into new markets
- Product Development– Introducing new products to an existing market
- Diversification– The concept of entering a new market with altogether new products
The Ansoff Matrix provides a framework for understanding different growth strategies, with each quadrant representing a specific level of risk and reward. The two dimensions of the matrix are Markets (Existing and New) and Products (Existing and New).
When we refer to Markets, it can have multiple interpretations. It can represent different geographical regions, such as the European market or the North American market. Alternatively, it can refer to specific customer segments or target markets based on demographics or preferences.
Let's explore the four growth strategies outlined in the Ansoff Matrix:
- Market Penetration: This strategy focuses on increasing sales of existing products in an existing market. The goal is to capture a larger share of the market by attracting more customers or encouraging existing customers to make repeat purchases. This strategy is considered relatively low risk as it leverages familiar products and markets.
- Market Development: In this strategy, businesses aim to expand their sales of existing products into new markets. This can involve entering new geographical regions or targeting different customer segments. Market development allows businesses to tap into untapped opportunities and reach a broader customer base. While it involves some level of risk, it can also lead to significant rewards.
- Product Development: This strategy involves introducing new products to an existing market. By expanding their product offerings, businesses can cater to the evolving needs and preferences of their existing customer base. Product development requires research, development, and innovation to create new offerings that resonate with customers. This strategy carries a moderate level of risk but can lead to increased market share and customer loyalty.
- Diversification: Diversification is the most challenging and high-risk strategy in the Ansoff Matrix. It involves entering new markets with entirely new products that may be unrelated to the existing business. This strategy requires significant investment, research, and development to establish a foothold in unfamiliar markets. While diversification offers the potential for substantial rewards, it also carries the highest level of risk.
By understanding the different growth options presented by the Ansoff Matrix, businesses can make informed decisions about their expansion strategies. It is essential to carefully assess the level of risk and reward associated with each strategy and align them with the business’s goals, capabilities, and market conditions.